Designing for the Metaverse: Opportunities and Challenges
Introduction
In recent years, the concept of the Metaverse has transcended its roots in science fiction and has begun to manifest itself as a tangible digital reality. With the rise of virtual and augmented reality technologies, the Metaverse is on the cusp of becoming a transformative force in our lives. As this digital universe takes shape, the field of Metaverse design is emerging, presenting both exciting opportunities and complex challenges. In this blog “Designing for the Metaverse: Opportunities and Challenges”, we will delve into the Metaverse, exploring its potential applications, essential design principles, and the critical ethical considerations that must guide its development.
The Metaverse: A Brave New Digital World

Before we dive into the design aspects, let’s clarify what the Metaverse is. The Metaverse can be described as a collective virtual shared space, merging physical and digital realities. It is a vast digital ecosystem where users can interact, create, work, and play, all within a seamless virtual environment. Think of it as the internet evolved into a fully immersive 3D experience, like something out of your favorite science fiction novel.
Potential Applications of the Metaverse
Social Interaction: One of the most immediate applications of the Metaverse is enhancing social interactions. Users can gather, communicate, and socialize as avatars in virtual spaces, breaking down geographical boundaries.
Education: The Metaverse can revolutionize education by creating immersive learning environments. Students can explore historical events, conduct virtual experiments, and interact with instructors and peers from around the world.
Workplace Collaboration: Businesses are already exploring the Metaverse as a platform for remote work and collaboration. Virtual offices and meeting spaces can provide a more engaging and productive work environment.
Entertainment and Gaming: The gaming industry has been a driving force behind Metaverse development. It offers new levels of immersion, storytelling, and interactivity, with possibilities ranging from live concerts to virtual theme parks.
Healthcare: Virtual healthcare consultations, therapy sessions, and even physical rehabilitation can be conducted in the Metaverse, providing accessible healthcare options.
Design Principles for the Metaverse
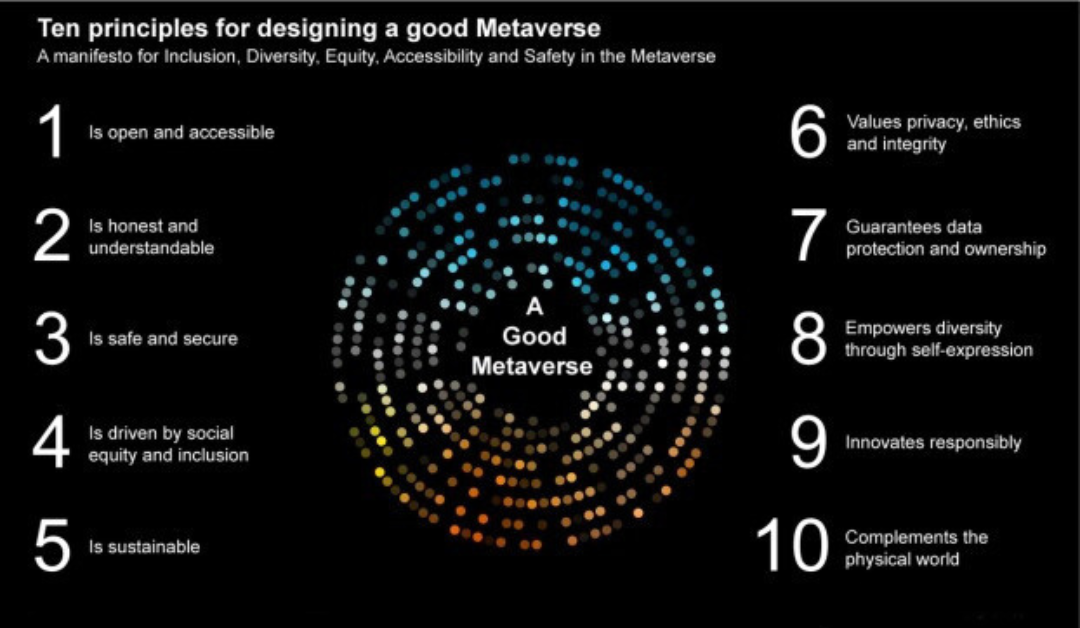
Creating a functional and engaging Metaverse requires careful consideration of design principles:
User-Centered Design: Like any digital platform, the Metaverse should prioritize user experience. User-friendly interfaces, intuitive controls, and accessibility features are crucial.
Interoperability: To ensure the Metaverse’s success, it should be open and interoperable. Users should be able to bring their digital assets, identities, and experiences from one virtual world to another.
Scalability: As the Metaverse evolves, it must be designed to scale seamlessly to accommodate a growing user base and expanding virtual spaces.
Privacy and Security: Protecting user data and privacy is paramount. Robust security measures, clear data policies, and user consent mechanisms must be in place.
Inclusivity: The Metaverse should be designed to cater to diverse populations. Considerations for people with disabilities, language diversity, and cultural sensitivity are essential.
Immersive Realism: Strive for high-quality graphics, realistic physics, and immersive audio to enhance the sense of presence within the Metaverse.
Ethical Considerations in Metaverse Design

As we venture into the Metaverse, ethical concerns become increasingly significant:
Digital Inequality: Not everyone has equal access to the Metaverse due to technology and economic disparities. Designers must work to bridge this divide and ensure inclusivity.
Privacy and Data Ethics: The Metaverse collects vast amounts of user data. Safeguarding this information and providing transparent data practices is crucial to prevent abuse.
Identity and Authenticity: The ability to create digital personas raises questions about identity and authenticity. Establishing trust and mitigating identity fraud are essential challenges.
Virtual Addiction: Just like the real world, users can become addicted to the Metaverse. Designers must consider measures to promote healthy usage and prevent overdependence.
Virtual Crime: As in any digital space, virtual crime and harassment can occur. Implementing systems to combat harassment and protect users is vital.
Content Regulation: Deciding what is permissible within the Metaverse raises complex questions about freedom of expression, hate speech, and violence. Striking a balance between freedom and responsibility is a significant challenge.
Conclusion
Designing for the Metaverse: Opportunities and Challenges:- The Metaverse represents an exciting frontier in digital design, with vast potential to transform how we live, work, and play. However, it comes with an array of challenges, from technical hurdles to profound ethical dilemmas. As designers and developers explore this brave new world, they must prioritize user-centric design, inclusivity, and ethical considerations. By doing so, we can ensure that the Metaverse becomes a space that enriches our lives, fosters creativity, and respects the rights and dignity of its users. As we embark on this journey into the Metaverse, it is essential that we navigate it with responsibility and foresight to create a truly extraordinary digital reality.







