Unveiling the Art and Science of Product Design in Mechanical Engineering
Unveiling the Art and Science of Product Design in Mechanical Engineering:- In the dynamic world of engineering, one term that frequently takes the center stage is “Product Design.” At first glimpse, this can be seen as only a blend of hardware; however, it is actually an interesting merger of art and technology’s elements. Over the last twenty years I have been working as a designer in mechanical engineering product design field. As far as this captivating issue is concerned, I ought to inform other individuals concerning the meaning of product design in these terms.
Defining Product Design

Product design is a vast domain dealing with the originating, growth, and improvement of tangible objects. The types of merchandise involved may vary, from basic items for use in everyday life to sophisticated machinery and systems. Mechanically, it is about shaping, designing or creating meaning for an idea.
In essence, product design aims at achieving a right mix of form with function. Engineering a working product is not enough; one needs to engineer a solution fitting into the users’ lives and environment in which the product will be operated.
The Core Principles

Functionality: Any product serves to accomplish some work or purpose in principle. The product designers in mechanical engineering minutely scrutinize its purpose, evaluating factors like loads, stresses, and motions. It is aimed at making certain that the commodity operates effectively and faithfully.
Ergonomics: Ergonomics is essentially important in designing products meant for human consumption or usage. Ergonomics attempts to produce equipment that is user-friendly and comfortable to use. Ergonomics encompasses things such as the positioning of buttons on smartphone or how shape of chair, among other.
Aesthetics: While functionality is paramount, aesthetics should never be underestimated. A product’s visual appearance can have a significant impact on how consumers perceive it and desire it. The product should work perfectly and be visually appealing.
Materials and Manufacturing: Materials and manufacturing approaches are important elements of products’ design. The materials used in the plant must be made of necessary mechanical properties, endurance, and economic efficiency. Additionally, understanding manufacturing processes ensures that the design can be translated into a real-world product efficiently.
Cost and Sustainability: Product design should have cost considerations. To achieve this, designers should aim at developing affordable products that maintain and enhance their functionality and quality of design. However, contemporary concerns include sustainability which has given rise to eco-designs amongst others.
The Design Process
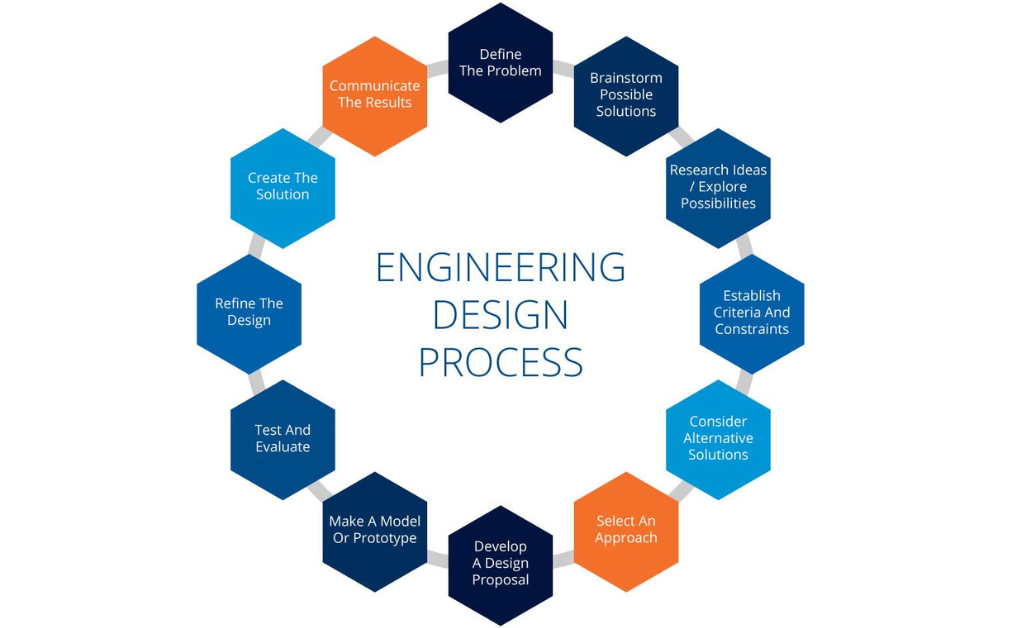
Now, let’s explore the intricate journey that a product takes from concept to reality. The product design process in mechanical engineering can be broken down into several key stages:
Conceptualization: It all begins with an idea. Whether it’s a revolutionary concept or an improvement on an existing product, this stage involves brainstorming, research, and sketching to define the product’s purpose and features.
Analysis: Before diving into detailed design, engineers conduct feasibility studies and analyze the product’s functionality. This involves mathematical calculations, simulations, and prototypes to ensure that the concept is viable.
Detailed Design: Details are added at this point in order to enrich the design. This is often done using Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software, which results in 3D models and technical drawings. During this stage one can pick out materials, set up the tolerances and make essential decisions concerning how the product can perform.
Prototyping: Building a physical prototype allows designers to validate their concepts. Prototypes help identify design flaws, assess ergonomics, and test functionality. It’s a crucial step in the refinement process.
Testing and Iteration: Prototypes are subjected to rigorous testing to ensure they meet performance criteria. Any issues that arise are addressed, and the design is iterated until it meets all requirements.
Manufacturing and Production: Once the design is finalized and tested, it’s time for mass production. Manufacturers follow the design specifications to create the product on a larger scale.
Quality Control: Quality control measures are implemented to maintain consistency and ensure that each product meets the established standards. This step is crucial for delivering reliable products to consumers.
Challenges and Innovations

Over the years, the field of product design in mechanical engineering has witnessed significant challenges and innovations. Here are a few notable ones:
Miniaturization: This has led to new extremes in miniaturisation as people have continued with a trend towards smaller, more compact devices like smartphone watches. However, small form factor design while retaining functionality has posed a considerable problem.
- Materials Advancements: New materials including carbon fibre composites and advanced polymers have opened up the avenues for design and made improvements in the product’s performance.
- Simulation and Modeling: Modern simulation and modelling tools have transformed product design. This allows engineers to perform simulations of how a particular product will work in different circumstances, resulting in sturdier designs.
The Future of Product Design in Mechanical Engineering

As we look to the future, several trends and developments are poised to shape the field of product design in mechanical engineering:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Engineers will use AI-driven design tools and generative design algorithms, driving engineers into optimizing designs quickly and effectively.
- IoT Integration: As a result, IoT will keep pushing for digital technology immersion in physical products to create intelligent and interconnected devices.
- Biomechanics and Biomimicry: Studying nature will apply concepts from biomechanics in generating novel design in products that will eventually result in better and eco-friendly solutions.
- Customization: The trend of personalization and customization will increase, resulting in products which are designed according to each person’s demand/choice.
- Human-Centered Design: As a result, designers will begin to look for ways and means to develop products geared towards improving the User Experience and enriching Quality Of Life.
Unveiling the Art and Science of Product Design in Mechanical Engineering:- In conclusion, product design in mechanical engineering is a captivating journey that combines technical expertise with artistic creativity. This is art that involves converting ideas into practicality, functionalism and beauty. In view of the continually changing face of technology and innovations, one can hope for still more interesting developments in the field of designing various products. Therefore, if you are interested in becoming a mechanical engineer or simply captivated by the secret of your everyday products, product design is an intriguing world of mechanism that one can never resist exploring.







